Liquidity is one of the most fundamental concepts in the Forex market. It applies to everything that happens within the markets-from the movement of prices to the execution of trades. For beginner and experienced Forex traders, knowing liquidity sweep is fundamental to making good decisions in trading. In this article, we will explain what liquidity is, its importance, types of liquidity, zones of high liquidity, and how to spot these zones with the skill of an experienced trader. Also, we will cover some of the common liquidity traps and provide some practical insights that can help improve your overall probability of winning trades.
What is Liquidity in Forex & Why Does It Matter?
Liquidity in Forex measures how easily the currency pair can be purchased and sold in the market without a visible impact on its price. In other words, it points to a liquid market in situations wherein tons of buyers and sellers operate at any given time.
Looking at it, the most liquid pairs such as the EUR/USD or GBP/USD are based on huge trading volumes. High liquidity conditions provide very low spreads, fast execution, and reduced slippage which help traders to be profitable.
Why Liquidity is Crucial in Forex:
For smooth trade execution and cost efficiency, a liquidity pool is important in the Forex market. In a highly liquid market, trades go smoothly and fast, with buyers and sellers available in large numbers at a given time. Fast execution of trades prevents traders from being subject to delays and slippage. It also prevents sudden volatility to a certain extent and contributes to more stable price movements. If the price movements are stable, chart patterns become clearer and assist technical analysis. Liquidity is needed for every trade to have the utmost confidence, low cost, and precision in the Forex market.
“Now that you understand its importance, let’s go deeper into the types of liquidity that drive the Forex market.”
The Two Types of Liquidity That Move the Market
There are two types of liquidity that will help you recognize market dynamics and make more informed trading decisions.
- Buy-Side Liquidity
- Sell-Side Liquidity
Buy-Side Liquidity
Buy-side liquidity refers to buying interest at a certain price level. It shows how many traders or institutions are ready to buy a currency pair when the price approaches a certain low level. In general, this acts as a support zone.
Example: A trader buys EUR/USD at 1.0800. If there are thousands of others buying at that level, the price is probably getting ready for an upward bounce because of buy-side liquidity pressure.
Sell-Side Liquidity
Sell-side liquidity indicates selling interest at a certain price. This shows that traders are waiting for higher selling points, hence the formation of resistance zones.
Example: If many institutions are looking to sell at USD/JPY 150.00, the price may stall or reverse there due to strong sell-side liquidity pressure.
The Four Major Types of Liquidity in Forex
By having a clear view of the various types of liquidity, one can develop more new strategies in Forex trading. Below are the four major types of liquidity in the market:
1. Market Liquidity
Market liquidity is characterized as the ease with which one can buy/sell currency pairs. It is in direct relationship with market depth, which is the number of orders at different price levels.
- Moderate liquidity exists for major pairs such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD.
- Exotic currency pairs such as USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR usually have very low liquidity and high spreads.
2. Funding Liquidity
These liquidity types relate to the ease of obtaining money market funds to be used for trades by traders and institutions. When we consider big institutions, we deal with interbank liquidity or margin funding in terms of funding liquidity.
- Funding liquidity may disappear during a financial crisis or central bank intervention.
- Another crucial element is leverage: Low leverage means more margin is required, thereby tightening funding liquidity.
3. Session Liquidity
The Forex market is 24 hours, but liquidity is dependent on the ongoing session:
- London Session: Most liquid owing to the overlap with other sessions.
- New York Session: Second most liquid of all trading sessions.
- Asian Session: Considered illiquid in general, except JPY and AUD pairs.
- Overlap Sessions (London + New York): They are the most active time resulting in explosive moves.
4. Pair Liquidity
Another consideration is that liquidity might vary greatly from one currency pair to another:
- High liquidity pairs: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY
- Medium liquidity pairs: NZD/USD, AUD/JPY
- Pairs with low liquidity: USD/MXN, USD/SEK
Pair liquidity might dictate the spread, volatility, and trade execution. Hence, traders need to choose a strategy that fits the characteristics of the pairs they are trading.
Why Liquidity is the Key to Winning Trades?
If you want to consistently win in Forex, understanding liquidity is a game-changer for you.
Better Entry & Exit Points
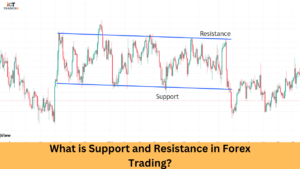
Points of liquidity are usually at support and resistance levels. Entering trades in the vicinity of these levels helps increase the odds of any success.
Reduced Slippage
With high liquidity, your orders would not experience too much slippage and would remain true to their desired price.
Best Risk Management
With liquidity, it becomes much easier for you to manage your stop-loss and take profit levels.
Institutional Behavior
In high liquidity areas, banks and hedge funds execute large orders to avoid influencing the market too much. Following their lead puts you one up.
How to Identify High-Liquidity Zones Like a Pro?
Now to trade like a pro let’s follow these steps to identify such liquidity zones.
Step 1: Observe Order Flow & Volume
Using volume profile, order book, or market depth indicators will show you where the big players are placing orders.
Step 2: Look for Areas of Price Rejection
You are looking for candles with long wicks or sharp rejections that denote a buy-side or sell-side liquidity.
Step 3: Consider Previous Highs & Lows
Institutional traders search out stop-loss clusters above recent highs or below recent lows. Such arrangements serve as hidden liquidity zones.
Step 4: Support & Resistance Levels
Historical price zones wherein high trading activity took place are often key liquidity pools.
Step 5: Be Mindful of the Event of News
Liquidity spikes often get triggered during major news releases like NFP, CPI, or interest rate decisions.
Common Liquidity Traps That Kill Your Trades!
Even experienced traders can fall victim to liquidity traps. Here are some common ones to avoid:
Fake Breakouts
This is the case where the price breaks through resistance and attracts buyers then the price reverses. The actual intent is to collect liquidity above the highs.
Stop-Hunts
On the other hand, price moves to place your stop loss by institutions to collect liquidity and later moves in the buy direction.
Idiosyncratic Market Hours
Trading in low-volume sessions will always see lower fillers and unpredictable results.
Choppy Consolidation Zones
Price moves in a tight range, sometimes between levels, to build up liquidity before a big move has happened. Don’t fall trapped in its trading noise.
Conclusion
Liquidity in Forex trading is more than just a buzzword. It is the pulse of the market. Drawing upon order flow, market depth, trading volumes, and volatility brings one great edge to both beginners and experienced traders.
Adopting the behavior of learning how to identify buy-side and sell-side liquidity, distinguishing between session-wise fluctuations and their common liquidity traps will sharpen the three areas of entry points, exit points, and trading performance.
FAQS
What is the most liquid currency pair in Forex?
The most liquid pair is the EUR/USD, given that global trade and financial transactions between the Eurozone and the U.S. are large volumes.
What is the consequence of a low-liquid environment in Forex trading?
In a low-liquid market, spreads will widen, slippage may increase, and price movement may work erratically, increasing the risk factor in trading.
Can liquidity be foreseen in Forex?
Yes, traders will foresee the entry and exit points of liquidity through volume data, historical price zones, and economic calendar events.
Does high liquidity always benefit the traders?
Not always. While it favors smooth execution, crowded trades may lead to sudden reversals. Market sentiment also becomes an important factor here.
Which tools are employed in liquidity analysis?
Popular tools include Volume Profile, Order Book, Depth of Market (DOM), and Footprint charts.