In the world of forex trading, understanding market inefficiencies and price imbalances is important for success. The ICT Fair Value Gap (FVG) is one of the popular trading strategies developed by Inner Circle Traders (ICT). Fair Value Gaps offer insight into institutional trading behavior and underlying market inefficiencies.
In this article, we will explain what ICT Fair Value Gaps are and how to identify them like a pro and finally the best strategies for trading them. From a beginner to an advanced trader, mastering Fair Value Gaps can improve one’s trading game to the next level.
Let’s dive into the world of smart money trading and uncover how Fair Value Gaps can transform your strategy from guesswork to precision.
What is ICT Fair Value Gap?
An ICT Fair Value Gap is a price imbalance or inefficiency that occurs when the market moves rapidly leaving behind unfilled orders between candlesticks. It typically happens during strong bullish or bearish movements where the price does not retrace to fill the missing volume.
In simpler terms, a Fair Value Gap represents a void or gap in price action areas where institutional traders are likely to return to complete their order flow. Traders use these gaps to predict potential reversal zones, retracement levels, or continuation patterns.
Fair Value Gaps are particularly useful in identifying potential entry and exit points in trading. They are often seen in conjunction with other ICT concepts like liquidity pools, order blocks, and market structure shifts.
The Mechanics Behind Fair Value Gaps
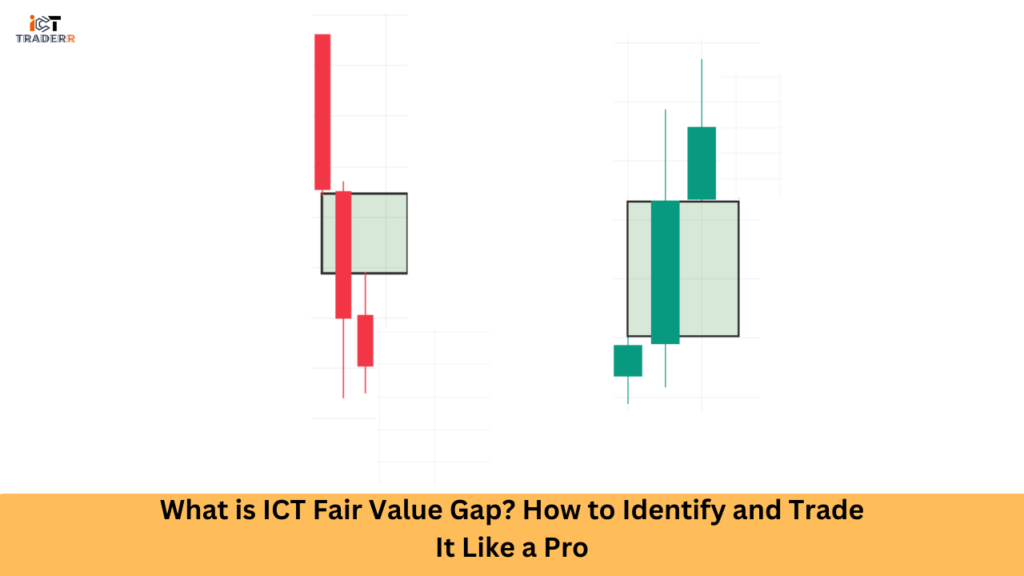
Understanding the mechanics of a Fair Value Gap in trading starts with the basics of candlestick structures. A Fair Value Gap forms when the price creates three consecutive candles, and the middle candle’s body (or wick) doesn’t fully overlap with the candles before and after it.
Example:
- The first candle moves in the direction according to trend.
- The second candle gaps up or down, creating an imbalance.
- The third candle continues in the direction of the trend, leaving the gap unfilled.
The gap between Candle 1’s high and Candle 3’s low becomes the Fair Value Gap.
This gap signals that the market moved too quickly, leaving behind unfilled buy or sell orders. Also a variation called implied FVG is critical., Institutional traders, banks, hedge funds, and Smart Money often revisit these levels to fill those orders, causing price retracement.
How to Identify ICT Fair Value Gaps Like a Pro
To trade ICT Fair Value Gaps effectively, you must learn to spot them accurately on the chart. Here’s how:
- Switch to a Higher Time Frame (HTF): FVGs on 1H, 4H, or daily charts are more reliable than on lower timeframes.
- Look for Imbalanced Price Movement: Find three-candle structures where the wicks do not overlap.
- Mark the Gap Zone: Highlight the area between the high of the first candle and the low of the third (for bullish moves) or vice versa for bearish moves.
- Wait for Price to Retrace: Patience is key—wait for the price to revisit the gap before entering a trade.
Tools to Use:
- TradingView for charting
- FVG indicator (optional)
- Fibonacci retracement (to confirm levels)
“Combine FVG analysis with order blocks, liquidity zones, and break of structure (BOS) for high-probability entries.”
Types of ICT Fair Value Gaps and Their Importance
Not all Fair Value Gaps are created equal. There are two primary types that you must understand:
Bullish Fair Value Gap
A bullish fair value gap appears when the price increases upward, creating an unfilled gap between the high of the first candle and the low of the third.
When to Use:
- During market uptrends
- To identify potential entry points after a retracement
- As a support zone
Characteristics:
- Indicates strong buying pressure
- Often followed by continuation moves
- Excellent for long trades
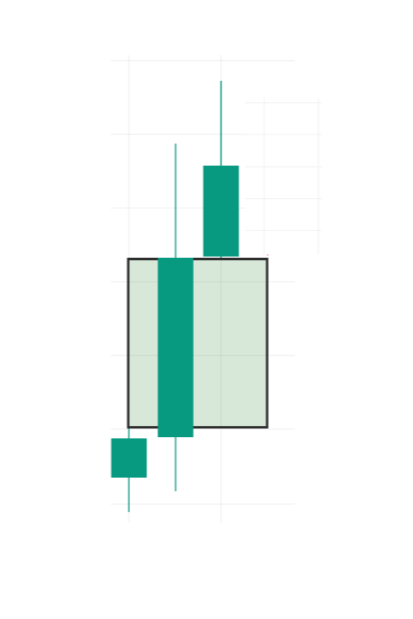
Bearish Fair Value Gap
A bearish fair value gap forms when the price drops significantly, leaving a gap between the low of the first candle and the high of the third.
When to Use:
- In a downtrend
- To predict possible price pullbacks before another sell-off
- As a resistance level
Characteristics:
- Represents intense selling pressure
- Frequently attracts sellers on retest
- Ideal for short positions
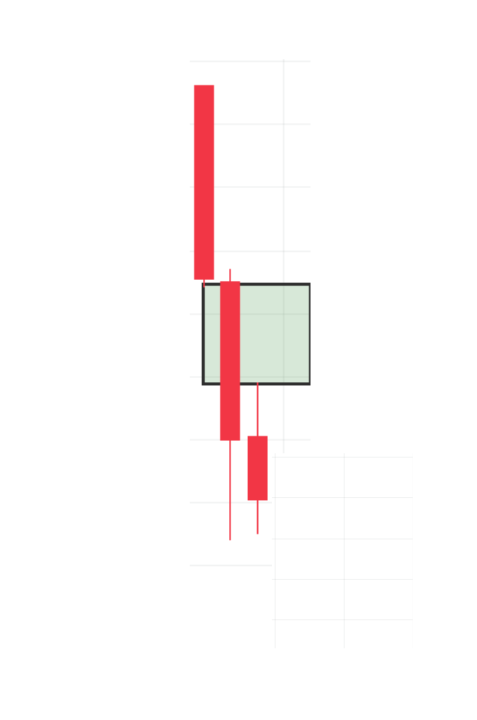
How to Trade ICT Fair Value Gaps Effectively
Trading ICT Fair Value Gaps involves a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Mark the FVG Zone
Use the three-candle rule and highlight the gap area with a box.
Step 2: Wait for Confirmation
Let the price retest the gap. Watch for rejection patterns like pin bars, engulfing candles, or lower time frame break of structure.
Step 3: Enter Trade with Precision
Place your entry at the edge or midpoint of the gap. Use tight stop-losses just beyond the gap zone to minimize risk.
Step 4: Set Risk-Reward Targets
Use Fibonacci levels, liquidity targets, or recent swing highs/lows to take profit.
Step 5: Manage Risk
Never risk more than 1–2% of your capital. Combine FVGs with confluences like market structure, institutional order flow, or liquidity zones.
Common Mistakes Traders Make with Fair Value Gaps
Even though Fair Value Gaps are powerful tools, many traders misuse them. Here are common mistakes to avoid:
1. Trading Every FVG
Not all FVGs are valid. Trade only those with confluence—like being near an order block or BOS level.
2. Ignoring Market Context
Always consider the overall market structure. A bullish FVG in a bearish trend is often a trap.
3. Entering Without Confirmation
Don’t enter blindly. Use candlestick confirmation or other price action techniques.
4. Overleveraging
Many traders overtrade FVGs with high leverage. Stick to sound risk management principles.
5. Relying on Indicators Alone
While FVG indicators can be helpful, manual identification is more reliable in volatile markets.
Conclusion
You now know that the ICT Fair Value Gap is not just a name; it is smart money trading that can give one an edge in strategy. Learning to identify these price gaps, analyze them, and then trade them gets you into the game with the institutional traders that move the market. Everyone either trades Forex, indices, or crypto. Incorporating FVGs into your strategy will improve clarity, risk-reward ratios, and less harsh mistakes.
“Like most things you will learn and have discipline and practice with, mastering Fair Value Gaps will make charts never look the same way again.”
FAQs
Is the ICT Fair Value Gap strategy suitable for beginners?
Yes, but it’s essential to understand price action basics and practice on a demo account first.
Which time frame is best for trading fair value gaps?
Higher time frames like 1H, 4H, or Daily provide more reliable signals.
Can I use indicators to find FVGs?
Yes, several indicators on TradingView can identify FVGs, but manual analysis is often more accurate.
Do FVGs work in crypto and stock markets?
Absolutely. The concept applies across all markets where price action and institutional behavior matter.
What’s the difference between a Fair Value Gap and a Liquidity Void?
Both represent price inefficiencies, but liquidity voids usually reflect larger-scale moves and less volume, while FVGs are more precise zones for potential retracement.