The Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm (IPDA ICT) is a forex trading model used by institutions to manipulate price movements and execute large orders efficiently. It helps forex, stocks, and futures traders spot key price levels, liquidity pools, and optimal trade entry points based on interbank trading strategies.
In this blog post, we will give an overview of the basic principles of the IPDA ICT methodology, how it can be applied in varied contexts of the market, and what it means for beginner and professional traders alike. By the end, institutional mechanisms in creating market movements should be clearer allowing you to potentially set yourself to profit from such moves.
What is the Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm (IPDA) ICT?
IPDA stands for Institutional Price Displacement Activity, which refers to a systematic process whereby institutional market participants such as banks, hedge funds, and large financial entities route their orders and manipulate price to achieve optimal execution. The term was created by Michael Huddleston, better known in trading circles as “ICT” (Inner Circle Trader). he developed this concept after years of market observation and analysis.
Very simply, IPDA is not an algorithm in the coding sense rather, it is a conceptual model that describes how smart money operates in financial markets. Its greatest contribution is in providing an understanding of:
- How large institutions create liquidity pools
- The manipulation tactics used to collect retail stop losses
- Price delivery mechanisms employed to reach institutional targets
- Market structure elements that signal institutional intent
IPDA differs from conventional technical analysis by focusing on order flow, market structure, and institutional behavior patterns rather than standard indicators. It proposes that price movements aren’t random but follow specific patterns designed to facilitate large order execution while minimizing market impact.
How Does IPDA Work?
IPDA works through a methodical process where institutional players create, manipulate, and exploit market conditions to facilitate their order execution. Unlike retail traders, who typically back momentum or follow technical indicators, institutions must solve a unique problem and how to buy or sell significant positions without adversely affecting the market.
The Core Mechanism
The basic IPDA process typically follows these stages:
- Accumulation/Distribution Phase: Institutions begin building or reducing positions at key market structure points, creating what ICT methodology calls “order blocks.”
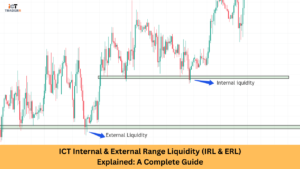
- Liquidity Engineering: Price is manipulated to areas where retail and smaller traders have placed stop losses or pending orders, creating pools of liquidity that institutions can use to fill their large orders.
- Displacement: Once sufficient liquidity is engineered, price rapidly moves away from the liquidity zone, often creating “fair value gaps” in the process.
- Order Fulfillment: The institution completes its order execution at predetermined target areas, often at significant support/resistance levels or previous market structure points.
- Equilibrium: The Price may then return to a balanced state until the next institutional requirement emerges.
Understanding IPDA Market Cycles
IPDA operates within specific market cycles that repeat across all timeframes. Understanding these cycles is important for successfully implementing an ICT methodology in your trading approach.
The Four Primary Market Phases
According to IPDA concepts, markets move through four distinct phases:
- Accumulation: Institutions quietly build positions while keeping prices within a relatively narrow range. This often appears as a sideways, seemingly directionless market to retail traders.
- Manipulation: Once sufficient positions are built, institutions engineer price movements to trigger retail stop losses and create liquidity for their larger orders.
- Distribution: Having achieved their position objectives, institutions begin to unload their holdings, often to retail traders who are now buying near market tops or selling near market bottoms.
- Expansion: Price moves strongly in the intended direction as institutional orders are fully executed and market participants react to the new price discovery.
Key Time-Based Strategies in IPDA
Time plays a crucial role in IPDA methodology, with specific periods offering enhanced insights into institutional activity. Understanding these time-based strategies can significantly improve trading precision.
London Kill Zone and New York Kill Zone
Two timeframes that are particularly important for ICT methodology:
London Kill Zone (LKZ)
The market opening period for London sessions (generally in the ranges of 3:00-5:00 AM EST), where European banks and financial institutions kick off their trading day and usually make some dramatic moves.
New York Kill Zone (NYKZ)
The market opening period for New York sessions (generally in the ranges of 8:00-10:00 AM EST), where US institutions enter the market to usually do some serious damage to the price.
These represent the periods of increased volatility and institutional activity, making it most suitable for viewing the actualization of those IPDA principles.
Asian Range and Premium/Discount Concepts
The Asian session period typically starting from about 7 p.m. till 2 a.m. EST usually gives good reference ranges that would be anticipated for subsequent market movements.
Asian Range
The high-to-low range coming out of the Asian trading hours usually holds strong as a reference for the next London and New York sessions.
Premium/Discount Levels
Prices traveling over the Asian range are said to be under “premium,” while prices down below the Asian range are classified under “discounts.” These two concepts help traders gauge if the price is overextended in one direction or is likely reversing.
Time knowledge also gives market structure-only foundations of how these time-based elements relate with contextual awareness to trading to improve decision-making.
How to Trade ICT IPDA Data Ranges?
Implementing IPDA concepts in actual trading requires specific techniques and approaches that differ from conventional trading methods.
Market Structure Analysis
Effective IPDA trading starts with proper market structure analysis:
- Multiple Timeframe Analysis: Begin by analyzing higher timeframes to identify key institutional levels, then drill down to lower timeframes for precise entry.
- Order Block Identification: Look for areas where the price shows a strong reaction, particularly the last candle before a significant move (often called the “last point of supply/demand”).
- Liquidity Identification: Map areas where retail stop losses are likely concentrated, typically just beyond recent highs and lows or key psychological levels.
- Fair Value Gap Recognition: Identify price gaps caused by imbalances between buyers and sellers, which often get filled in subsequent price movements.
Entry and Exit Strategies
IPDA-based trading employs specific entry and exit techniques:
- Optimal Trade Entry (OTE): Enter trades at refined zones where the price is likely to reverse, often at the intersection of multiple technical factors.
- Strategic Profit Targets: Set targets based on known institutional levels rather than arbitrary pip counts or risk-reward ratios.
- Stop Loss Placement: Position stops where they’re less likely to be triggered by institutional liquidity sweeps.
- Equal Highs and Lows Strategy: Pay particular attention to areas where price creates multiple highs or lows at the same level, as these often represent liquidity pools that institutions target.
Risk Management & Psychological Aspects
Trading with IPDA methodology requires not only technical understanding but also robust risk management and psychological discipline.
Risk Management Principles
Effective risk management within the IPDA framework includes:
Position Sizing: Limiting exposure to a small percentage of trading capital per trade
Asymmetric Returns: Seeking trades with greater potential reward than risk
Correlation Management: Avoiding overexposure to correlated market moves
Scenario Planning: Having contingency plans for various market reactions
Psychological Challenges
The psychological aspects of IPDA trading can be particularly challenging:
Contrarian Thinking: IPDA often requires trading against what seems obvious to the retail crowd
Patience: Many high-quality setups require extended waiting periods
Discipline: Adhering strictly to predefined rules without emotional interference
Confidence: Trusting the methodology even during inevitable drawdown periods
Successful IPDA traders develop mental frameworks that support these psychological requirements, often through detailed journaling, regular review, and continuous education.
Conclusion
The Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm (IPDA), as instructed by ICT trading methods, gives an appropriate framework to understand the way the institutions work with price action. By learning market cycles, liquidity mechanics, and time-based strategies, you can improve your accuracy in predicting price movements.
With an understanding of IPDA data ranges, fair value gaps, and order blocks, traders can carry out trades that have a higher probability of success while minimizing their risk. However, success in ICT trading demands patience, discipline, and a good risk management program.
The incorporation of these IPDA ICT principles allows traders to move from retail-based trading methodologies toward an institutional-level perspective and gain a competitive edge in the forex markets.
FAQs
What is the goal of this entire IPDA ICT framework?
The aim is to help traders understand how price delivery and manipulation occur so that they can trade in line with smart money.
What does IPDA do for traders?
IPDA enables traders to locate liquidity zones and fair value gaps, and recognize institutional order flow, thereby improving their chances of speculating on price movement direction with accuracy.
What is a fair value gap (FVG) in ICT trading?
A Fair Value Gap is a high-speed price imbalance, suggesting that the market is likely to come back to that price level to mitigate such inefficiencies.
What is the importance of time-based analysis in the IPDA?
Institutional traders work on specific time frames, namely during events like the London Open and New York Open, thus, these time frames are considered the best for high-probability trades.
Can a beginner use the IPDA ICT strategy?
Yes, they are well off learning the building blocks- market cycles, liquidity grabs, and risk management before stepping into advanced trading techniques.