In modern trading, especially when navigating volatile forex or crypto markets, understanding ICT (Inner Circle Trader) concepts can significantly improve your accuracy and consistency. These principles are rooted in institutional trading logic, allowing traders to interpret price action with much deeper insight. Mastering a few core ICT concepts is essential if you want to boost your trading accuracy.
Let’s explore the top 5 most important ICT concepts every serious trader should know, followed by a section on combining them into one powerful strategy.
1. Market Structure (CHoCH & BOS)
Market structure is the basis for technical analysis and smart money trading. Two crucial ICT components of market structure are:
- Change of Character (CHoCH)
Think of this as the market whispering that something’s changing. When a previous trend begins to break down say, a series of higher lows is interrupted by a lower low that’s CHoCH. It’s often the first sign that a reversal is brewing.
- Break of Structure:
Break of Structure, occurs when price breaks a significant swing high or low, indicating that the current trend will continue.
By identifying CHoCH and BOS on your charts, you can align yourself with institutional order flow, enhancing your trading precision and decision-making. This structure-based approach filters out false signals and sharpens your trade entries and exits.
2. Liquidity Pools
Liquidity is what drives the markets. Stop-loss orders accumulate in liquidity pools, usually around swing highs and lows. Institutions hunt for these pools to fill large orders without causing slippage.
There are two main types of liquidity pools:
- Buy-side liquidity (above resistance levels)
- Sell-side liquidity (below support levels)
Retail traders often get trapped when their stop-losses are taken, and the market reverses. By identifying where liquidity resides, you can position your trades with the smart money, not against it.
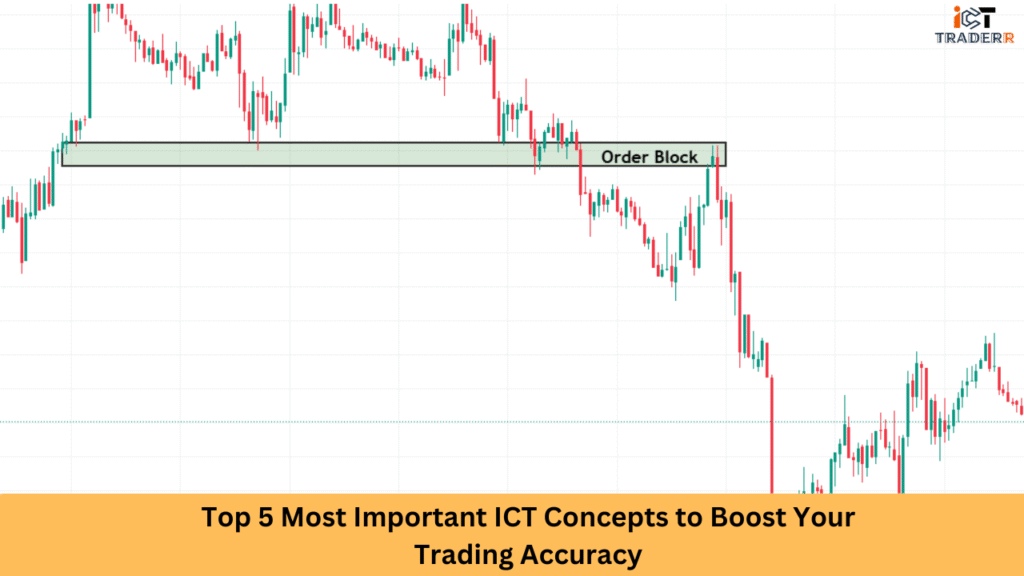
3. Order Blocks
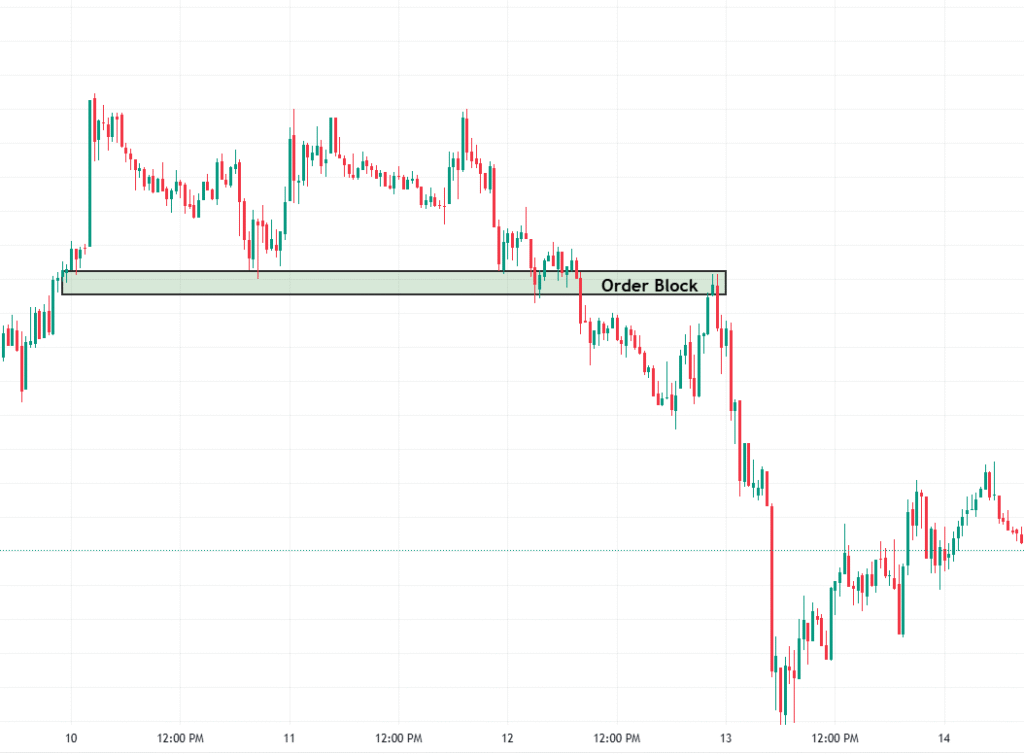
Order blocks are the footprints institutions leave behind. They’re essentially the last significant candle (often a down candle before a rally or an up candle before a drop) where a large player placed an order that shifted the market.
Traders using ICT methodology treat order blocks as high-probability zones for entry or reversal. When price returns to these zones, it often reacts strongly, offering precise entry points with tight stop-losses.
Types of order blocks include:
- Bullish Order Block: A down candle that occurs before an uptrend
- Bearish Order Block: An up candle that occurs before a downtrend
Trading from these zones offers an edge, especially when combined with CHoCH and liquidity pools.
4. Fair Value Gaps (FVGs)
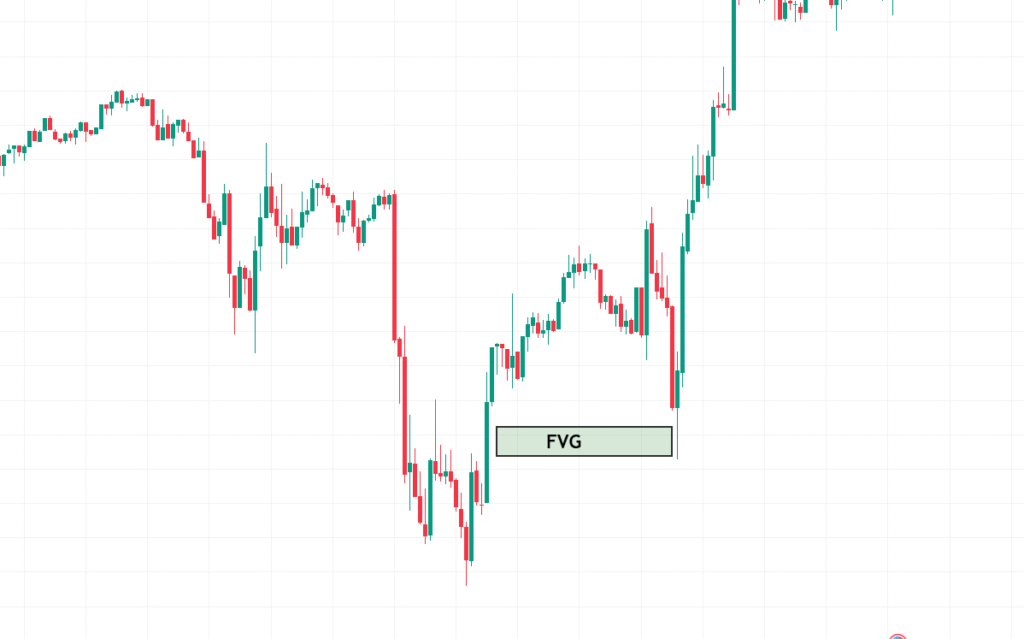
Fair Value Gaps are imbalances in the market caused by sudden price movement, leaving a “gap” between candles that wasn’t properly filled. According to ICT, price is likely to return and fill this gap before continuing in its direction.
FVGs are powerful because they show:
- Market inefficiency
- Potential retracement zones
- Ideal sniper entries when paired with order blocks
Traders can avoid entering overextended moves and wait for the price to “correct” to a fair value by recognizing FVGs. This is particularly useful in forex trading, where volatility often creates such gaps.
5. SMT Divergence
Divergence, known as SMT (Smart Money Technique), occurs when correlated assets act differently at crucial market points. This divergence often signals potential reversals or manipulations by institutional players.
For example:
- EUR/USD makes a higher high
- GBP/USD makes a lower high
The divergence might indicate that the trend is weakening or about to change. SMD divergence is stronger with liquidity grabs or CHoCH as further confirmation for the entry.
How to Combine These ICT Concepts in One Strategy
Now that you understand each ICT concept individually, here’s how to combine them into a cohesive strategy:
Step-by-Step Strategy:
- Start with Market Structure
BOS and CHoCH can be used to determine trend direction-observe for possible reversal.
- Mark Liquidity Pools
Identify visible retail stop zones above the highs or below the lows.
- Identify Order Blocks
Look for the last candle before a significant move in the direction of your bias. - Locate Fair Value Gaps
Confirm if the price is likely to return to that zone. Wait for retracement. - Check SMT Divergence
To validate trade direction and avoid traps, use correlated pairs.
Once all elements align, you have a high-probability trade backed by smart money principles.
Example Trade Setup:
- EUR/USD is in a bullish BOS
- Price just swept liquidity below a major low.
- Approaching a bullish order block + FVG
- SMT Divergence shows GBP/USD is lagging
- Result: High-confidence long entry
Conclusion
Mastering these 5 top ICT concepts, market structure, liquidity pools, order blocks, fair value gaps, and SMT divergence has a very significant influence on one’s trading performance. They put you into the perception of the market from the angle of institutions alone and not merely retail indicators. No matter what you’re trading in, forex, crypto, or indices, these ideas show where to start when it comes to precision with trading, reducing the false signals, and improving the overall consistency.
Practice these concepts together, backtest them on historical charts, and gradually integrate them into your live trading.
FAQs
Are ICT concepts only for advanced traders?
Not at all. Even if you’re new to trading, these ideas can simplify what feels confusing if you take the time to study and apply them one at a time.
Are ICT strategies suitable for day trading?
Absolutely. ICT concepts like liquidity pools and order blocks work well on lower timeframes like M5, M15, or H1.
Do I need special indicators for ICT?
No. ICT trading is primarily based on price action and smart money theory, requiring clean charts and keen observation, not complicated indicators.
Do I need special indicators?
Nope. Clean charts, patience, and a solid understanding of price action are all you need.