If you are new to trading concepts, especially those introduced by ICT, you might be wondering, What is an ICT vacuum block? Our comprehensive article for newcomers will explain everything you need to know about ICT vacuum blocks, including their functions, types, trading strategies, common blunders, and frequently asked questions (FAQs).
What Is an ICT Vacuum Block?
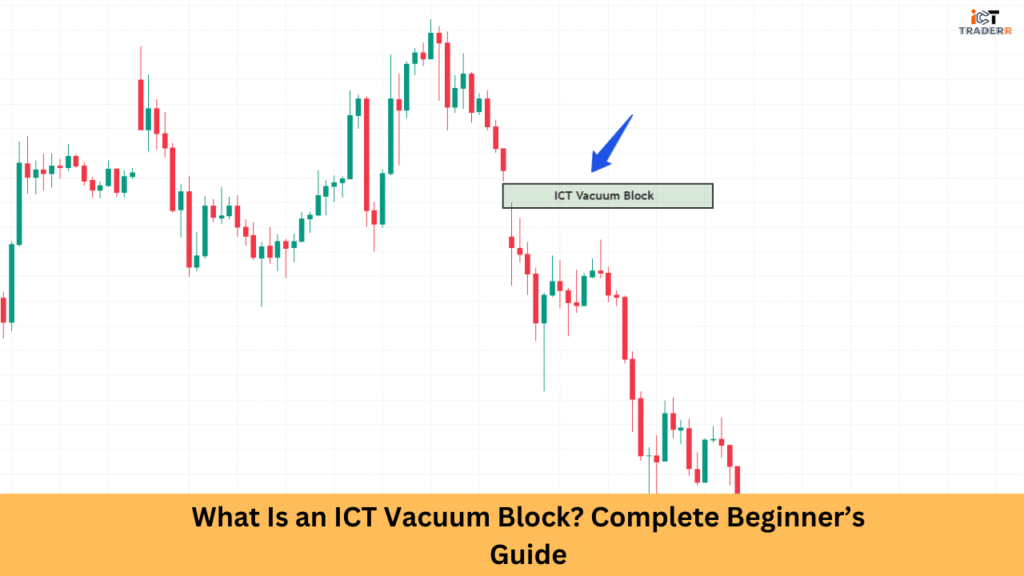
An ICT Vacuum Block is a technical price structure identified in financial charts where price makes a rapid, significant move in one direction, leaving behind an area with minimal trading activity. It is this “vacuum” that leads to a condition of imbalance between buyer and seller and is seen to bring prices back to fill this vacuum later.
The blocks are said to come after institutional players (i.e. banks, hedge funds) have quickly accumulated or distributed a position creating an effect where price moves rapidly down or up several price levels.
Before continuing the trend, institutional and bank traders with smart money frequently return to these gaps to “fill the imbalance.
The Logic Behind Vacuum Blocks
The foundation of vacuum blocks lies in market psychology and institutional order flow. Here’s why they matter:
- Order Flow Imbalance: When large institutional players enter or exit positions rapidly, they create an imbalance in orders, leading to sharp price movements.
- Market Efficiency: Markets naturally seek efficiency and tend to return to areas of previous imbalance to “test” those levels.
- Liquidity Hunting: Institutional traders often place orders in areas of previous inefficiency, which becomes a magnet for future price action.
- Price Discovery: Vacuum blocks represent areas where proper price discovery didn’t occur, creating a natural tendency for prices to revisit these zones.
The psychological aspect is significant in retail, you often chase momentum, while institutional traders wait for opportunities to enter at optimal price levels. Vacuum blocks create these optimal entry zones for smart money participants.
Types of ICT Vacuum Blocks
There are mainly two types of ICT vacuum blocks based on market direction:
1. Bullish Vacuum Block
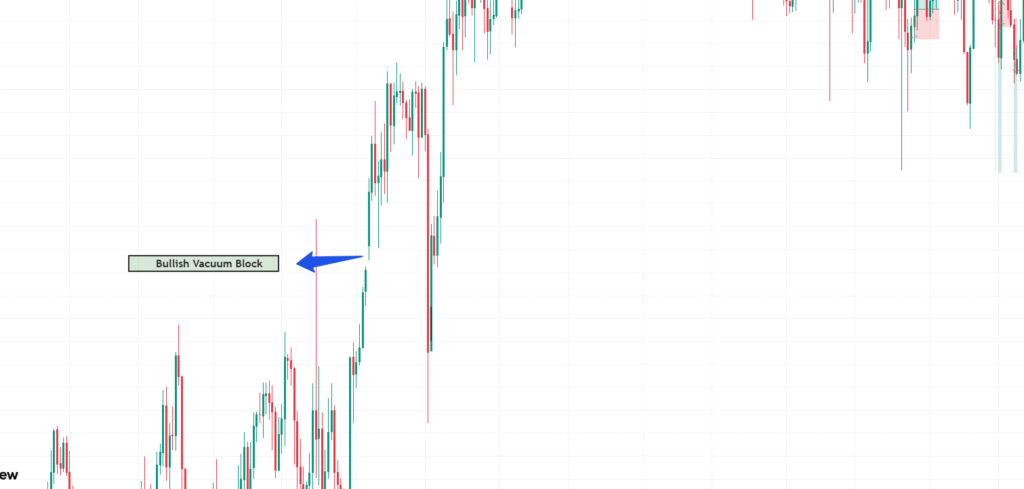
A bullish vacuum block forms when price makes a rapid upward movement, leaving a void below. This structure suggests potential downward price movement in the future to fill the vacuum.
2. Bearish Vacuum Block
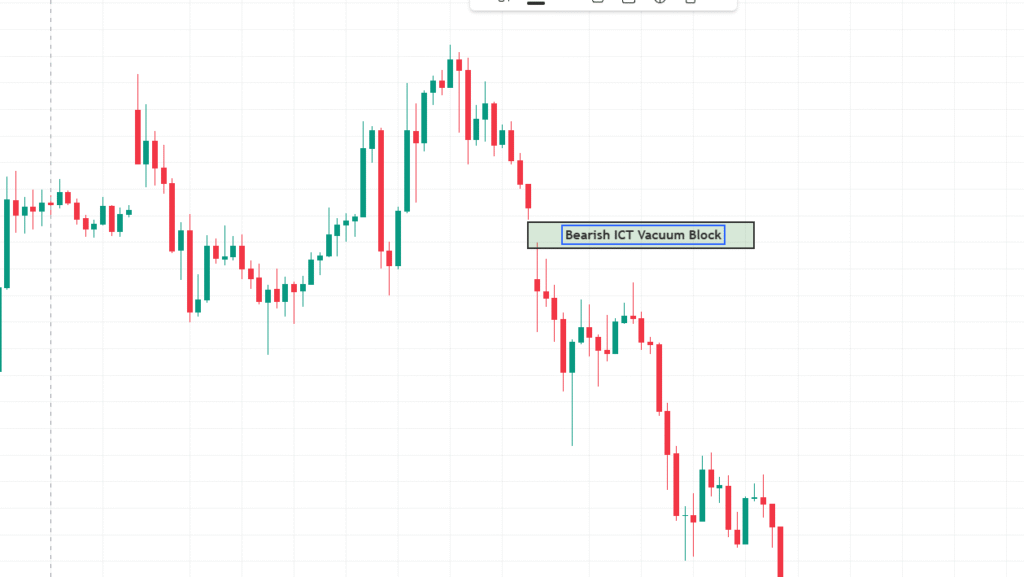
A bearish vacuum block forms during a strong bearish move (aggressive selling). The price retraces upwards into the vacuum before resuming downward.
Both types offer excellent opportunities if you understand how to enter correctly.
How to Trade ICT Vacuum Blocks
To trade ICT vacuum blocks successfully, you need a systematic approach:
- Identify the Vacuum: Look for long candles without wicks or gaps in price action.
- Mark the Block: The second chart depicts the area where the price begins to jump aggressively.
- Wait for Retracement: Let price come back into the vacuum zone.
- Confirm Entry: Look for confirmation signals (like order blocks, breaker blocks, or market structure shifts).
- Manage Risk: Always use proper stop-loss and take-profit rules.
Trading Bullish ICT Vacuum Block (Step-by-Step)
Here’s how to trade a bullish vacuum block:
Identify a bullish vacuum block where the price has moved up rapidly.
From the beginning to the end of the rapid movement, draw the vacuum zone.
Waiting for a price retracement back to the vacuum area follows.
Look for rejection candles or bullish order blocks at the lower portion of the vacuum.
Enter long positions when the price shows confirmation of support at the vacuum zone.
Place a stop-loss order below the vacuum block’s lowest point.
Target Profit should be made at the previous swing high or the next significant level of resistance.
Consider partial profit-taking at key resistance levels.
Trading Bearish ICT Vacuum Block (Step-by-Step)
Here’s how to trade a bearish vacuum block:
Identify a bearish vacuum block where the price has dropped sharply.
Mark the vacuum zone from the starting point of the rapid price movement to its end
Wait for a price rally into the vacuum zone.
Look for rejection patterns or bearish order blocks at the upper portion of the vacuum.
Enter short positions when the price shows confirmation of resistance at the vacuum zone.
Place the stop-loss above the vacuum block’s highest point.
Profit target the previous swing low or the next significant support level..
Consider scaling out of positions at key support levels.
Key Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced traders make errors when trading vacuum blocks. Here are common mistakes to avoid:
Trading in isolation:
Never trade vacuum blocks without considering the broader market context and trend.
Premature entries:
Patience is crucial, wait for confirmation before entering trades based on vacuum blocks.
Improper stop placement:
During normal market fluctuations, placing excessive stops can result in premature exits.
Ignoring the timeframe confluence:
Vacuum blocks are more reliable when they appear across multiple timeframes.
Overlooking market structure:
Always consider whether a vacuum block aligns with or contradicts the prevailing market structure.
Neglecting risk management:
No matter how appealing a vacuum block trade may appear, you should never put more than 1% to 2% of your trading capital at risk.
Confirmation bias:
Don’t force vacuum block patterns where they don’t exist just to validate your trading bias.
Conclusion
Understanding and trading ICT vacuum blocks can drastically improve your success rate if done correctly. By recognizing price inefficiencies, waiting for proper retracements, and trading with confirmation, you align yourself with how smart money moves. Remember: the key is not just spotting a vacuum but also trading it with precision and risk management.
Practice on demo accounts, journal your trades, and soon you’ll master this powerful concept!
FAQs
Are ICT vacuum blocks only for Forex trading?
No, vacuum blocks can be found across multiple markets, including Forex, crypto, stocks, and indices.
Can I use indicators to find vacuum blocks?
While manual identification is better, tools like imbalance indicators can help, but should not be solely relied upon.
How long does it take for the price to revisit a vacuum block?
There is no fixed time. It can happen within minutes on lower timeframes or days on higher timeframes.
Is trading vacuum blocks risky?
Yes, however, using proper strategies and risk management can minimize potential losses.